The SEO Guide to Links
What is a Link?
A link (officially called Hyperlink, but almost everyone just uses "link") is a reference to another webpage that is a clickable element on a webpage that when clicked will take you to another webpage.
What are the types of link?
In SEO we refer to links with a few different names depending on where they originate from and where they point to. The following diagram shows the different types of link:
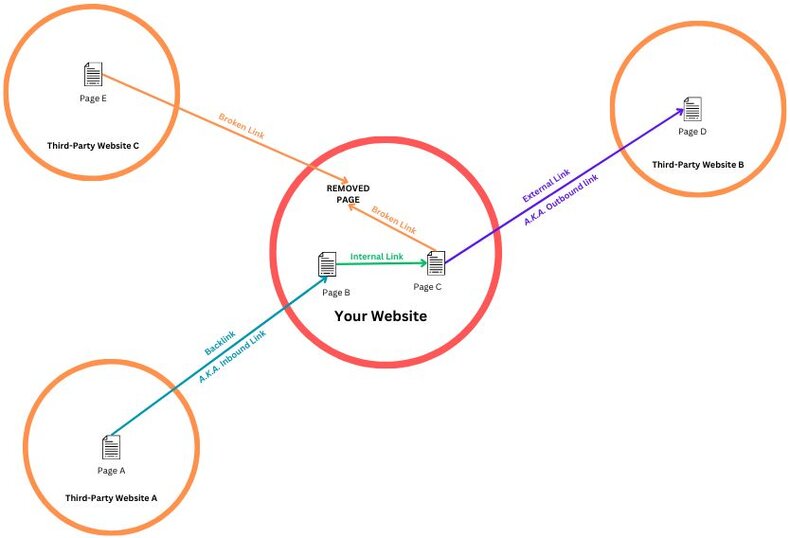
Backlink
A backlink (also known as an inbound link) is a link from a page on a third party website to a page on your website.
On the diagram we can see a backlink (shown in blue) from Page A on Third Party Website A to page B on Your Website.
Internal Link
An internal link is a link from a page to another page on the same website
On the diagram we can see an internal link (shown in green) from Page B to Page C on Your Website.
External Link
An external link (also known as an outbound link) is a link from a page on your website to a third party website.
On the diagram we can see an external link (shown in purple) from Page C on Your Website to page D on Third Party Website C.
Broken Link
A broken link is a link from any page that points to a page that no longer exists, the link is broken.
On the diagram we can see two broken links (shown in orange). The first from Third party
Link Relationship Attributes
Links themselves can have relationship attribute information added to them. This relationship attribute data allows us to give Google some extra information as to what kind of link it is.
The link attribute options we have are:
Sponsored
If you have a commercial relationship with the page you are linking to then you should use the sponsored attribute. You are saying to Google that you’ve either been paid to place this link, or you may benefit in some way from traffic that follows this link, such as if there is an affiliate relationship.
Google will not pass any PageRank to links marked as sponsored which means the page receiving the link won’t get any SEO benefit from the link. You’ll also protect both the linking page and the linked to page from any kind of penalty for link selling.
The HTML for a sponsored link would look like:
<a rel=”sponsored” href="https://domain.com">this is a sponsored link</a>
Ugc
If the link has been placed in any user generated content (such as a forum or post comment) then you should apply the ugc attribute. The ugc attribute tells Google that it wasn’t the site owner or page author that placed the link but rather a user of your site, meaning that you can’t directly vouch for the destination page.
Google will make its own determination whether to count these links for SEO purposes, it also gives the linking site some protection should the link be to a site that Google views negatively.
The HTML for a ugc link would look like:
<a rel=”ugc” href="https://domain.com">this is a ugc link</a>
Nofollow
The nofollow attribute predates the sponsored and ugc attributes. You can use the nofollow attribute in both the circumstances that you use sponsored and ugc to benefit from the same protections each offer.
You can also use a nofollow link if you want to link to a third party site but for whatever reason you don’t want your link to help them rank better, such as if you wanted to link to a page which you disagree about the content of.
The HTML for a sponsored link would look like:
<a rel=”nofollow” href="https://domain.com">this is a nofollow link</a>
Followed link
A followed link is one to which we don’t add any attribute data to, some people call these “dofollow’ links as they are the opposite of a nofollow link. Google will take this as meaning there is no commercial relationship that caused the link to be created and that you wish to pass PageRank to the destination page.
The HTML for a followed link would look like:
<a href="https://domain.com">this is a followed link</a>